Parar, arrancar, habilitar y deshabilitar Firewalld en Centos 7
Hoy quiero explicaros rápidamente como podéis manejaros con vuestro Firewalld o Iptables en vuestro Centos 7. Os explico cómo pararlo, arrancarlo, habilitarlo o deshabilitarlo. Pero también intentaré explicaros rápidamente como generar reglas concretas vía comando.
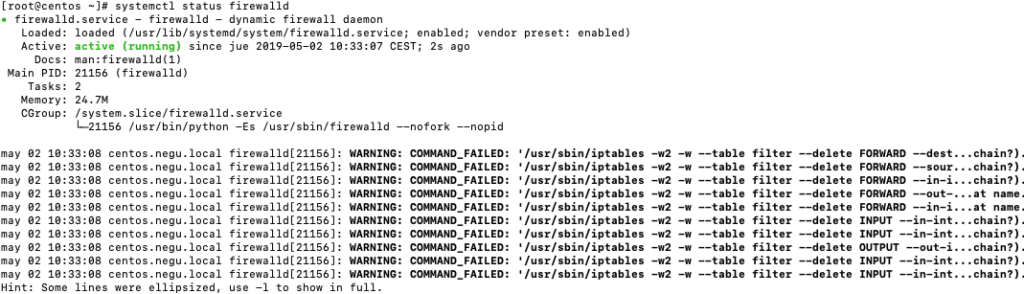
Status firewalld / Iptables en Centos 7
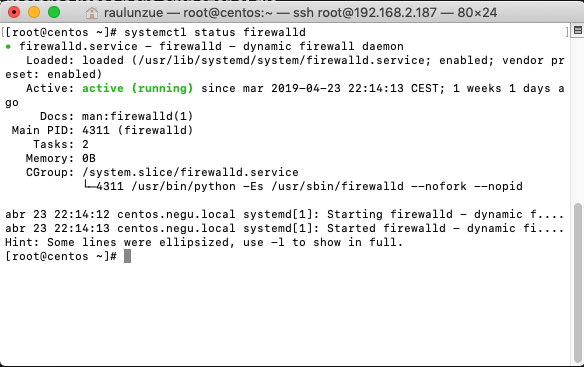
Lo primero que haremos es chequear el estado del demonio o servicio con el siguiente comando. Lo haré con root en mi caso:
|
1 |
systemctl status firewalld |
Si está habilitado, podemos lanzar una revisión de las reglas con:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
[root@centos ~]# iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination ACCEPT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:domain ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:domain ACCEPT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:bootps ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:bootps ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere INPUT_direct all -- anywhere anywhere INPUT_ZONES_SOURCE all -- anywhere anywhere INPUT_ZONES all -- anywhere anywhere DROP all -- anywhere anywhere ctstate INVALID REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited ------ |
Stop firewalld / iptables en Centos 7
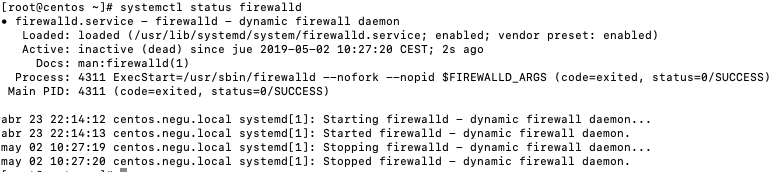
Para parar nuestras iptables o firewall en Centos 7 simplemente lanzamos:
|
1 |
systemctl stop firewalld |
Disable firewalld para Centos 7
Parar nuestras iptables no implica que en el arranque vuelvan a arrancarse. Para deshabilitarlas lanzamos:
|
1 |
systemctl disable firewalld |
Enable firewalld para Centos 7
Y para habilitarlas usaremos:
|
1 |
systemctl enable firewalld |
Start firewalld para Centos 7
Para arrancar el firewall nuevamente:
|
1 |
systemctl start firewalld |
Crear reglas firewall en Centos 7
Tenéis dos opciones comunes para crear reglas de iptables en Centos 7. Por un lado estaría instalar firewall-cmd y crear una regla de la siguiente forma, por ejemplo:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
# Instalación firewall-cmd yum install -y firewall-cmd # Crear regla firewall firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http --permanent # Guardar cambios firewall-cmd --reload # Verificar cambios firewall-cmd --zone=public --query-service=http |
O directamente con el comando iptables:
|
1 2 |
iptables -I INPUT 7 -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -j DROP -p tcp --destination-port 110 -i eth0 -d 192.168.2.10 |
¿Te ha gustado la entrada SÍGUENOS EN TWITTER?
¿Te ha gustado la entrada SÍGUENOS EN TWITTER O INVITANOS A UN CAFE?
 Blog Virtualizacion Tu Blog de Virtualización en Español. Maquinas Virtuales (El Blog de Negu) en castellano. Blog informática vExpert Raul Unzue
Blog Virtualizacion Tu Blog de Virtualización en Español. Maquinas Virtuales (El Blog de Negu) en castellano. Blog informática vExpert Raul Unzue





Felicitaciones Raul, excelente informacion, me sirvio de mucho.
Me gustria contactar contigo, necesito soporte virtual para CENTOS 7 y quisieras aber si te einteresa
GRACIAS
SALUDOS