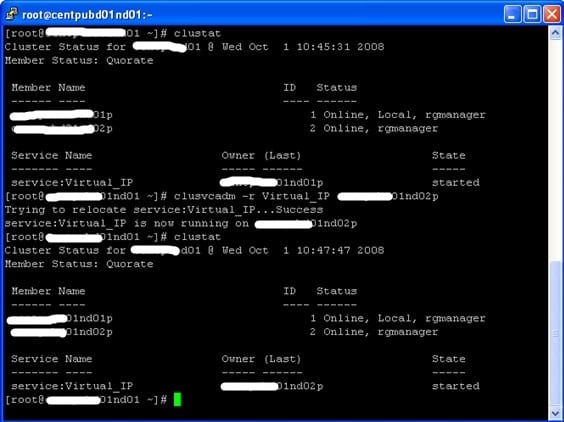
Clustat
clusvcadm [-d <service> ] [-e <service> ] [-l] [-u] [-S] [-m <member> ] [-r <service> ] [-S] [-R <service> ] [-s <service> ] [-v]
The clusvcadm command allows an administrator to enable, disable, relocate, and restart user services in a cluster. In order to perform cluster service operations, the cluster daemons must be running (and have quorum) on the member system on which the command is invoked.
Opciones
-d <service>
Stops and disables the user service named service
-e <service>
Enables and starts the user service named service
-l
Lock the local resource group manager. This should only be used if the administrator intends to perform a global, cluster-wide shutdown. This prevents starting resource groups on the local node, allowing services will not fail over during the shutdown of the cluster. Generally, administrators should use the clushutdown(8) command to accomplish this. Once the cluster quorum is dissolved, this state is reset.
-m <member>
When used in conjunction with either the -e or -r options, this specifies the preferred target member on which to start the service.
-r <service>
Relocates the user service named service to another cluster member.
-R <service>
Restarts the user service named service on the cluster member on which it is currently running.
-S
Display whether each of the active service managers is locked or not. This can be used to verify the correct operation of the -l and -u options, but is only useful for debugging.
-s <service>
Stops the service named service until a member transition or until it is enabled again.
-u
Unlock the cluster’s service managers. This allows services to transition again. It will be necessary to re-enable all services in the stopped state if this is run after clushutdown.
EJEMPLO:
¿Te ha gustado la entrada SÍGUENOS EN TWITTER O INVITANOS A UN CAFE?
 Blog Virtualizacion Tu Blog de Virtualización en Español. Maquinas Virtuales (El Blog de Negu) en castellano. Blog informática vExpert Raul Unzue
Blog Virtualizacion Tu Blog de Virtualización en Español. Maquinas Virtuales (El Blog de Negu) en castellano. Blog informática vExpert Raul Unzue